What is the Difference Between a BNC and a Coaxial Cable?

20
Jun
 Coaxial Cable Assembly
Coaxial Cable Assembly
 Microwave Test Cable
Microwave Test Cable
 Coaxial RF Connector
Coaxial RF Connector
 Coaxial RF Adapter
Coaxial RF Adapter
 Coaxial RF Termination
Coaxial RF Termination
 Coaxial RF Test Probe
Coaxial RF Test Probe
 Coaxial RF Attenuator
Coaxial RF Attenuator
 RF Switches
RF Switches
 Rotary Joints
Rotary Joints
 Coaxial RF Power Dividers
Coaxial RF Power Dividers
In industries like telecommunications, broadcasting, and security, terms like “BNC” and “coaxial cable” are common, yet often misunderstood. A key tool in navigating these components is the BNC coaxial cable adapter, which ensures seamless connectivity across diverse equipment. This article explores the distinction between a BNC and a coaxial cable by posing the question, analyzing their roles, and resolving the confusion—equipping B2B professionals with clear, actionable insights.
Understanding the relationship between BNC connectors and coaxial cable forms the foundation for reliable system integration. Our precision-engineered BNC-BNC cable assemblies deliver robust coaxial connectivity for industrial applications, supported by clear coaxial vs bnc analysis to guide procurement decisions. This technical resource specifically examines the implementation of bnc connector to coaxial cable solutions and bnc to coaxial adapter components with secure-lock interfaces, demonstrating how advanced mechanical construction and rigorous validation testing ensure stable signal transmission, effectively suppress EMI/RFI interference, and maintain vibration-resistant performance where connection integrity is paramount. Discover industrial-grade bnc connector to coaxial cables systems engineered for flawless signal routing in complex enterprise environments and learn how our methodology exceeds industry standards in mechanical durability, electrical consistency, and operational lifespan, ultimately reducing system downtime and optimizing total cost of ownership through superior connection reliability and simplified maintenance procedures.
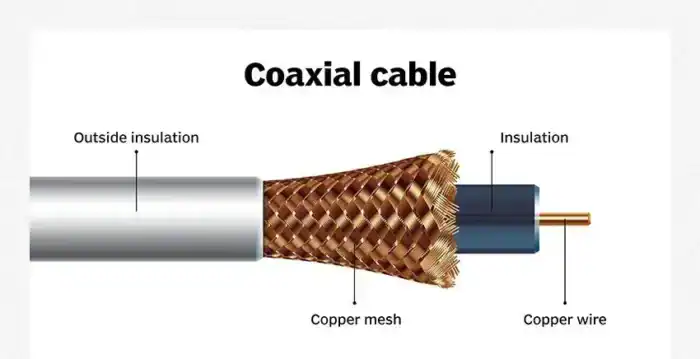
A coaxial cable is an electrical cable designed to carry high-frequency signals with minimal loss. It features:
Used in TV, internet, and RF applications, coaxial cables support various connectors, not just BNC.

BNC (Bayonet Neill-Concelman) is a connector type, not a cable. It attaches to coaxial cables, featuring:
Unlike the cable, BNC is the interface linking devices.
Adapters like the coaxial to BNC adapter or coaxial cable to BNC connector are critical when connectors don’t match.
A coaxial cable transmits signals, while a BNC connector enables device attachment. A “BNC cable” is simply a coaxial cable with BNC ends. Understanding this prevents miscommunication in procurement or setup.
Adapters ensure compatibility. Consider:
A BNC to coaxial cable adapter enables a secure connection between a security camera’s BNC output and an F-type monitor input, effectively converting between connector types while maintaining signal integrity. It provides a reliable, impedance-matched link crucial for professional surveillance installations, ensuring stable video transmission.
Drawing on our range of BNC cable coaxial and bnc connector for coaxial cable products, we deliver clear signals and broad device compatibility across industrial automation, broadcast, and telecommunications. Our precision-engineered BNC cable coaxial assemblies fix common connectivity issues, eliminate ground loops, enhance EMI shielding, and protect signal integrity over long distances. The bnc connector for coaxial cable utilizes a secure bayonet twist-lock for vibration-resistant performance in demanding sites, while maintaining precise 50-ohm or 75-ohm impedance to minimize reflections. These reliable bnc to coax cable solutions effectively bridge legacy system ports with modern RF equipment. We support integration with custom assemblies, on-site termination, documentation, and engineering resources to streamline architecture, reduce installation time, and ensure long-term operational uptime. Available bnc to rf cable types are designed to match specific bandwidth, impedance, and environmental requirements, helping to lower MTTR and total lifecycle costs. They also simplify field diagnostics, reduce spare parts inventory, and prevent intermittent failures in critical data and video links.
You can find high-quality BNC adapters like the bnc to coax adapter and bnc female to coax male adapter on brand websites.
 Coaxial Cable Assembly
Coaxial Cable Assembly
 Microwave Test Cable
Microwave Test Cable
 Coaxial RF Connector
Coaxial RF Connector
 Coaxial RF Adapter
Coaxial RF Adapter
 Coaxial RF Termination
Coaxial RF Termination
 Coaxial RF Test Probe
Coaxial RF Test Probe
 Coaxial RF Attenuator
Coaxial RF Attenuator
 RF Switches
RF Switches
 Rotary Joints
Rotary Joints
 Coaxial RF Power Dividers
Coaxial RF Power Dividers Coaxial Cable Assembly
Coaxial Cable Assembly
 Microwave Test Cable
Microwave Test Cable
 Coaxial RF Connector
Coaxial RF Connector
 Coaxial RF Adapter
Coaxial RF Adapter
 Coaxial RF Termination
Coaxial RF Termination
 Coaxial RF Test Probe
Coaxial RF Test Probe
 Coaxial RF Attenuator
Coaxial RF Attenuator
 RF Switches
RF Switches
 Rotary Joints
Rotary Joints
 Coaxial RF Power Dividers
Coaxial RF Power DividersNo account yet?
Create an Account